A version of this post was first published on January 4, 2019, in the Opinion section of Utility Dive.
The electric utility industry is abuzz with terms like blockchain and hosting capacity analysis. While the industry is certainly likely to hear more about these topics in the coming year, applications will likely be isolated to a few states in 2019.
The sector is undergoing change and we can expect a few larger, national trends to manifest. From changes in the resource mix to federal shakeups, here are six electricity trends to keep an eye on in 2019:
1. Coal continues to decline:
Coal’s decade long decline will continue in 2019. Four gigawatts (GW)are already committed to retirement and industry analysts project more than that will come to fruition by the end of 2019.
But coal retirements will only account for a portion of year-on-year coal consumption reductions.
Reduced generation from operating plants will be the main driver for reduced consumption. More coal plants will follow the recent trend to switch to seasonal operations because it isn’t economic to operate them year-round. Those that do operate year-round will do so at lower levels, barring a polar-vortex like event.
2. Renewables keep up the momentum:
There are more than 15 GW of utility-scale wind and solar trying to become operational in 2019. If federal tax credits become permanent, it would alleviate some of the pressure to get built in 2019. But regardless, renewables should be able to regain the title as the number one source of new capacity additions.
The industry should also expect some projects to come in at record low prices, despite tariffs. 2019 will also see the installation of the 100th GW of wind in the US and the 4th consecutive year where developers hit 10 GW of solar installations (including residential, commercial and utility scales).
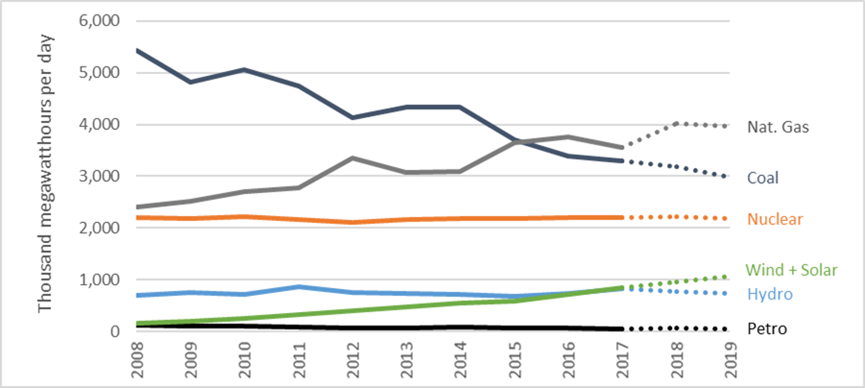
3. The rush to overbuild build gas:
When it comes to gas, the utility industry is repeating past mistakes, ignoring both the environmental costs and lack of public support for natural gas generation (unless you count paying for a supporting cast).
2019 will see a continuation of the trend to overbuild and over-rely on gas.
EIA tracks developer plans to build new natural gas combined cycle (NGCC) projects; separately, it projects how much is needed based on economic modeling. Comparing those two data sets reveals that the utility industry is poised to build three-times more NGCC capacity than is necessary. The overbuild in gas plants and infrastructure could lead to over $100 billion in stranded assets, which will either be recovered on the backs of ratepayers or investors.

4. Storage in the spotlight:
2018 was the year of storage headlines, particularly when it came to the record low prices of storage. Swaths of analyses have shown that utility-scale storage could replace gas peakers.
Whether on its own or paired with other resources, storage has piqued the interest of regulators and resource planners alike. Expect more announcements by savvy utilities committing to new storage projects.
However, if utilities don’t begin to recognize the full value stack of storage, then storage will struggle to reach its potential. Luckily, storage has bipartisan support, keeping the door open for state and/or federal legislation in this area.
5. Resource plans all around:
At least 30 states will see at least one electric utility with a resource plan in 2019 (including states with an expected ruling on an already filed plan).
Notable states to watch include Minnesota (where Xcel just committed to 100% carbon-free energy by 2050), Virginia (where the commission rejected the 2018 IRP and ordered the utility to file a better plan) and Mississippi (where the commission is in the process of finalizing new rules that could precipitate a new round of utility resource plans this year).
Expect these analyses to show that many coal plants aren’t economic and to focus on how utilities should replace coal.

6. New FERC faces, same hot topics:
A lot of the most contentious topics discussed at FERC in 2018 aren’t resolved, and we can expect those issues to spill over into 2019.
Fuel security, resiliency, storage, pipelines, PURPA, capacity market reforms, energy market reforms, and federal bailouts, are likely to show up before the agency in 2019.
It is worth noting there could be a new face (or two) at FERC: Commissioner LaFleur’s term is up in 2019 and with the recent passing of Commissioner McIntyre, changes to the agency’s makeup are inevitable. With Commissioner McNamee’s recent confirmation, the industry is watching to see how a changing commission handles the industry’s hottest topics.

